Digital art emerged with the first computers. Artists began to draw in graphic editing apps using tablets. Musicians began to record their works digitally. There is great convenience in the digital domain: digitized music is easier to process, deliver to the listener, and distribute.
Thanks to the Internet, copies of a music track can be instantly distributed all over the world. But there’s a problem: it’s difficult to know which are copies, and where and which is the original, as well as who the author or owner is. NFT technology helps to confirm the rights to a work of art.
Details about the technology, how it works, and the reasons for its sudden popularity, are all explained in detail in our article «A guide to NFTs: how they work, where to buy them, and whether you can make money from them.«
How the NFT confirms authorship of the music
NFT technology is based on blockchain technology. A blockchain is a single database, comprised of a chain of «blocks» of information. A blockchain stores information regarding all transactions made with tokens. For example, when a band releases a new album in the NFT format, a record of token creation appears in the blockchain. If they then sell an album to listeners — a record of ownership transfer appears for each sale. The blockchain allows for anyone to view the chain and see the path of a tokens from creation of the NFT to current owners.
Information in a blockchain is distributed and immutable: the record of artwork owners is stored in a common database that is stored simultaneously on multiple computers. In this way it cannot be deleted, altered, or tampered with.
The same principles underlie the cryptocurrency system. The difference is that cryptocurrency tokens are the same as money: one bitcoin is identical to another and worth exactly the same. NFT crypto coins are called non-interchangeable because they are as unique as the artwork itself.
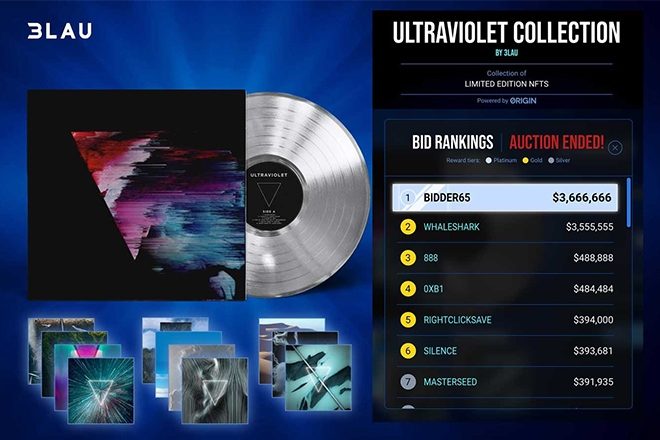
What NFT musicians are releasing
Any original object in the field of digital art can be turned into an NFT: a song, an album, a video clip, souvenirs with the artist’s logo, and even lifetime concert tickets. The author creates an NFT token, puts it up for sale at a fixed price or auction, and customers buy it for personal use or resale.
In January 2022, for example, Melos Studio released an NFT collection in memory of the legendary David Bowie. The collection consists of 12,000 unreleased photographs, audio recordings of the star’s monologues, unique videos, and one unreleased song.

Benefits of NFT music
| Before NFT | After the advent of NFT |
| To achieve popularity, musicians need intermediaries, such as music labels like Sony Music and Universal Music Group. The companies choose the most promising artists, sign licensing agreements with them, and are responsible for releasing, promoting, and distributing the music. The intermediaries get their share, which reduces the musicians' profits. | Musicians can sell and distribute their music as NFT tokens without intermediaries. They get all the profits from the sale, royalties from each resale, and license fees. For example, Rarible has a license fee of up to 10%. Even novice artists have a chance to succeed. |
| Music spreads on the Internet at an enormous rate, generating an unlimited number of pirated copies of tracks. Musicians are not remunerated for illegal music. Additionally, pirated music is hard to trace, and very difficult to prove in court. | It’s too early to say if this new NFT technology will eradicate piracy, but the technology does have that potential. Each token has a unique identification code: whoever created the NFT can prove copyright rights to it, and whoever bought a copy can also prove ownership. If a musician sells a limited-edition album, the blockchain can trace the path of each copy, and reliably determine which ones are legal and which are pirated. The author is guaranteed to receive remuneration both from the initial sale, and from each resale. On the other hand, NFT-platforms do not yet know how to check if a person who creates tokens owns the copyright. For example, OpenSea and Rarible do not verify NFT authors. |
| Fans of musicians collect autographs, concert posters, and photos. The possibilities of traditional collecting are somewhat limited. | NFT technology expands the possibilities for collecting and rewarding fans. You can tokenize anything, such as the right to get new releases before the rest of the audience, exclusive interviews, and unpublished photos of stars from concerts. |
| When people buy music through paid streaming services like Spotify and Apple Music, they only get the right to listen to it. The rights to commercial use of original recordings belong to authors or labels, but not to private customers. | By purchasing a token, a user simultaneously accepts the terms of a smart contract. It can contain any terms one desires. For example, a buyer might not only get the right to listen to and resell the music, but also the right to use it commercially. |

How to buy music NFTs
1. Get a digital wallet for storing cryptocurrency and NFT
A simple and inexpensive solution is to create a hot wallet using an application or special program, such as Coinbase Wallet, Trust Wallet, or MetaMask for example. This is convenient and inexpensive, but there is a risk that the data will be lost in the case of a hacker attack.
It’s recommended to store large amounts of currency and expensive NFTs in something called «cold wallets». These are separate devices like flash drives with serious protection, encryption, and passwords.
You can read about how OrbitSoft customized the currency display and appearance of the MyEtherWallet-based crypto wallet personal account in the article «Case study: How OrbitSoft Customized a Crypto Wallet for a Platform with Adult Content».
2. Choose a site to buy NFT music
The largest NFT-marketplaces are subsections of cryptocurrency exchanges Crypto.com, Binance NFT, and specialized platforms like OpenSea, Rarible, and Nifty Getaway. They can trade primary and secondary placements of tokens. If a token is sold by a musician-author, it’s a primary placement. If they are resold by token buyers, it’s a secondary placement.
The price of NFT is fixed or determined during the auction. One pays for one’s purchase with cryptocurrency through the app or a private wallet. Some sites allow for payment to be made with payment cards in dollars, for convenience.
Marketplaces take commissions. For example, at Rarible both the seller and the buyer pay 1% of the transaction amount. Etherium marketplaces also charge what is called a «gas» fee. These are payments to ensure the operation of the cryptocurrency generation program. On OpenSea, for example, the gas payment can be made once, or you can pay a small amount for each NFT purchase. The cost of gas can change a lot during the day, so these payments can eat up all the profits from a transaction.
3. Place a bet and wait for the NFT to appear in your wallet
On the marketplace, tokens have a fixed value, or it can be determined through an auction. For example, to buy a token on OpenSea, you need to go to the token’s page and click «Buy Now». An adjacent button is «Make an offer.» A buyer clicks this if they want to offer the seller their price. If both parties reach an agreement, the purchase transaction commences. When this happens, the NFT will appear in the buyer’s wallet.
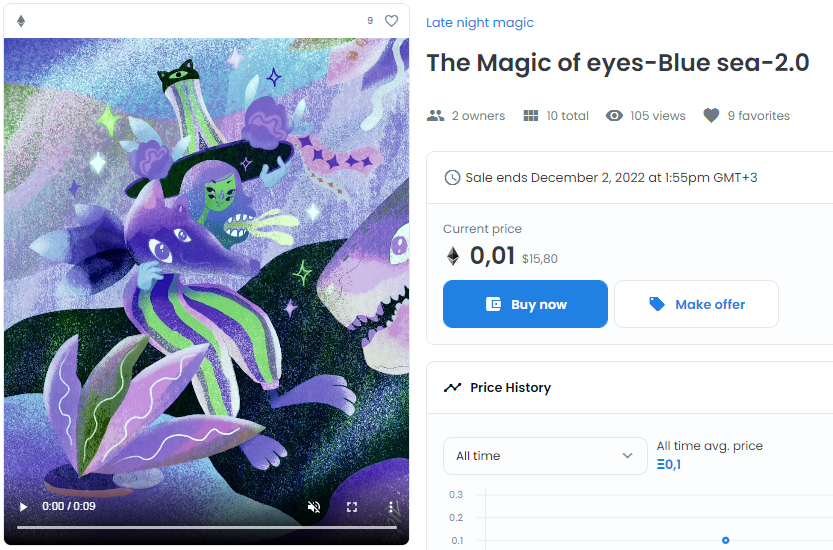
NFT-music is a risky investment
If we consider an NFT-token as an object for investment, we should remember that its profitability is ensured only by the community’s trust. The value of an NFT-token is the amount in cryptocurrency that other market participants are willing to offer for it, while collectors, fans, and traders are guided by their subjective opinion when buying it. The profit will go to the one who can predict the success of a work or performer.
OrbitSoft has developed a bot that can predict cryptocurrency rates and increase traders' profits
